- Conduct Wildfire Simulations
- Optimize Weather Stations
- Weather Station Application
- Open Source Materials
- Pilot Upper-Air Profiler
The PyreCast platform provides three wildfire forecasting tools for enhanced wildfire situational awareness covering the continental US including:
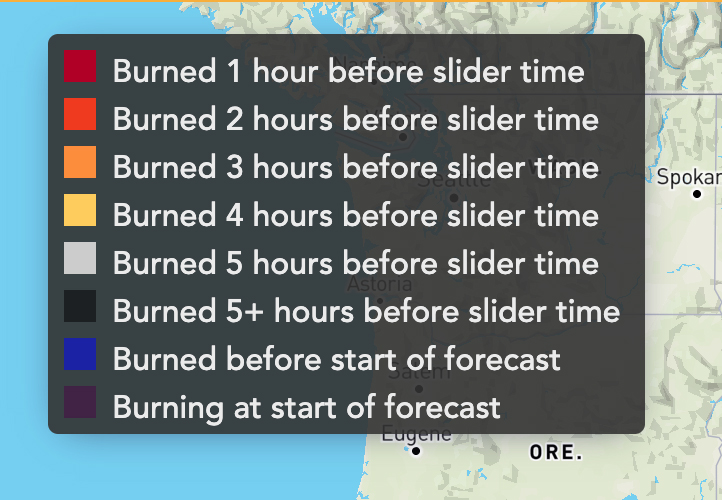
This tool provides 14-day fires spread forecasts for significant active fires within continental US. Active fire areas are established and recalibrated approximately every 12-hour from satellite-based heat detection data and fire spread is modeled using two different deterministic wildfire behaviors models (ELMFIRE and GridFire).
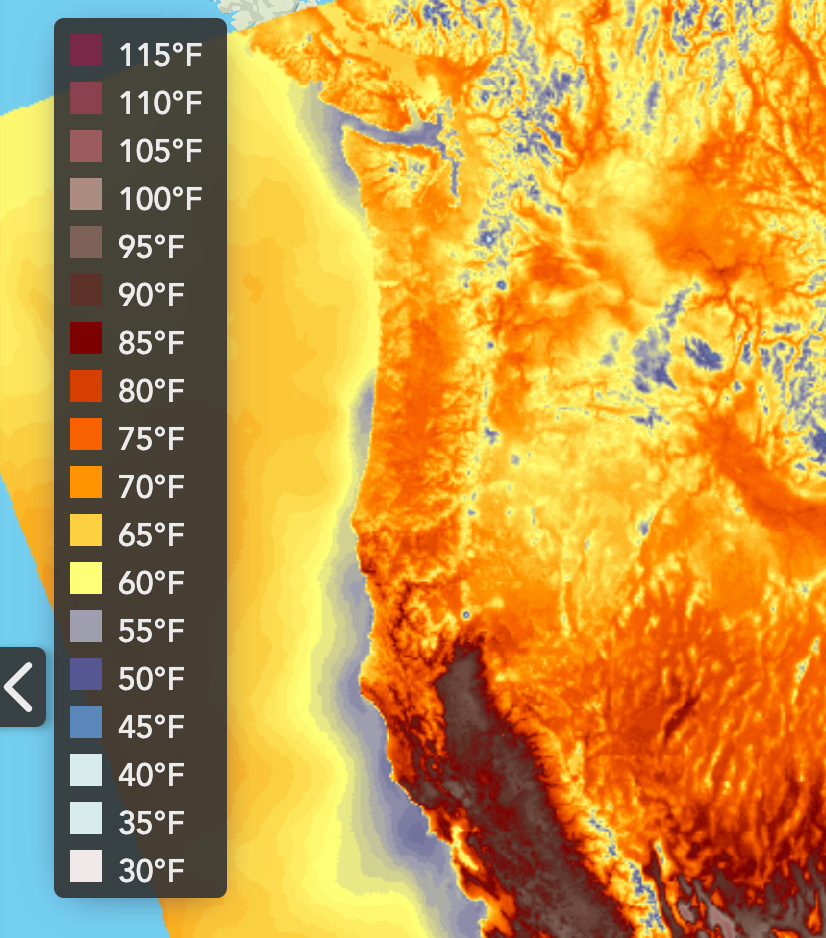
This tool provide access to seven different gridded weather forecast models having different spatial resolutions (1.33 km to 26 km) and forecast durations (15 minutes to 16 days). Each model provide access to up to fourteen fire-relevant weather variables and indices, including for example:
This tool provides 14-day fires spread forecasts for significant active fires within continental US. Active fire areas are established and recalibrated approximately every 12-hour from satellite-based heat detection data and fire spread is modeled using two different deterministic wildfire behaviors models (ELMFIRE and GridFire).

Dr. Saah has been broadly trained as an environmental scientist with expertise in a number of areas including: landscape ecology, ecosystem ecology, hydrology, geomorphology, ecosystem modeling, natural hazard modeling, remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS) and geospatial analysis. He has used these skills to conduct research primarily at the landscape level in a variety of systems. Dr. Saah has participated in research projects throughout the United States and Internationally. His academic research uses integrated geospatial science for multi-scale mapping, monitoring and modeling of environmental spatial heterogeneity, particularly in riparian, savanna, and forest ecosystems. These efforts include quantification of change in landscape pattern, investigating the linkages between pattern and processes, and understanding the pattern-process dynamic within different environmental management regimes. To complement this, Dr. Saah’s consulting research interest and experience include: developing holistic decision support systems for resource management, assessing natural hazards, and quantifying ecosystem service valuation. In addition, all of his research addresses access, availability, and accuracy of geospatial and environmental datasets, and scale in natural resource and environmental research. Dr. Saah is committed to producing high quality research projects that integrate the most current science and technology. He is dedicated to the accurate dissemination of results from these endeavors through innovative presentations, publications, and workshops.
Shane leads the Tahoe-Sierra Team at SIG. Shane is a Wildlife Biologist with more than 25 years of professional natural resources management, policy and research experience in the public, private and non-profit sectors. His experience is broad and includes managing the design and implementation of a status and trend monitoring and evaluation program, leading regional natural resource planning efforts, managing improved forest management carbon projects, aquatic plant monitoring and mapping, life cycle assessment, GIS analysis and drone imagery collection, managing wildfire risk research projects, preparing and reviewing environmental documents, and conducting a variety of wildlife investigations (e.g., home range, habitat use, food habits, disease). Prior to joining Spatial Informatics Group, he was the Science, Monitoring and Evaluation Program Manager for the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency and was the Wildlife Program Manager for the US Forest Service. Shane has a BS majoring in Wildlife and a MS majoring in Natural Resources from Humboldt State University.